
 |
| Home | Teacher | Parents | Glossary | About Us | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Definición formal de laintegral: a = x0 < x1 < x2 < ... < xn = b d = max (x1-x0, x2-x1, ... , xn - x(n-1)) x(k-1) <= X(k) <= x(k) k = 1, 2, ... , n 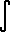  F '(x) dx = F(b) - F(a) (Teorema fundamental para
integrales de derivadas)
F '(x) dx = F(b) - F(a) (Teorema fundamental para
integrales de derivadas)
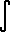 a f(x) dx = a a f(x) dx = a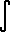 f(x) dx (si a es una constante)
f(x) dx (si a es una constante)
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|