|
|
|
Fourier Transform
 Definition of
Fourier Transform Definition of
Fourier Transform
f(x) = 1/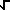 (2 (2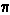 ) )
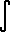  g(t) e^(i tx) dt
g(t) e^(i tx) dt
 Inverse Identity
of Fourier Transform Inverse Identity
of Fourier Transform
g(x) = 1/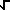 (2 (2 ) )
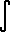  f(t) e^(-i TX) DT
f(t) e^(-i TX) DT

Fourier Sine and Cosine Transforms
 Definitions
of the Transforms Definitions
of the Transforms
f(x) = 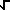 (2/ (2/ ) )
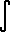  g(x) cos(xt) DT (Cosine Transform)
g(x) cos(xt) DT (Cosine Transform)
f(x) = 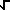 (2/ (2/ ) )
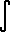  g(x) sin(XT) DT (Sine Transform)
g(x) sin(XT) DT (Sine Transform)
 Identities of
the Transforms Identities of
the Transforms
IF f(x) is even, THEN FourierSineTransform(
FourierSineTransform(f(x)) ) = f(x)
IF f(x) is odd, THEN FourierCosineTransform( FourierCosineTransform(f(x))
) = f(x)
Under certain restrictions of continuity.

|
|
|


 Definition of
Fourier Transform
Definition of
Fourier Transform Inverse Identity
of Fourier Transform
Inverse Identity
of Fourier Transform Definitions
of the Transforms
Definitions
of the Transforms Identities of
the Transforms
Identities of
the Transforms