
 |
| Home | Teacher | Parents | Glossary | About Us | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Cosine: Overview
The cosine (abbreviated "cos") is a type of trigonometric function. Definition 1 is the simplest and most intuitive definition of the cosine function. It basically says that, on a right triangle, the following measurements are related:
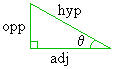 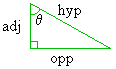
Furthermore, Definition I gives an exact equation that describes this relation: cos(q) = adjacent / hypotenuseThis equation says that if we evaluate the cosine of that angle q, we will get the exact same value as if we divided the length of the side adjacent to that angle by the length of the triangle's hypotenuse. The relation holds for any right triangle, regardless of size. The main result is this: If we know the values of any two of the above quantities, we can use the above relation to mathematically derive the third quantity. For example, the cosine function allows us to answer any of the following three questions: "Given a right triangle, where the measurement of one of the non-right angles (q) is known and the length of the side adjacent to that angle q is known, find the length of the triangle's hypotenuse." "Given a right triangle, where the measurement of one of the non-right angles (q) is known and the length of the triangle's hypotenuse is known, find the length of the side adjacent to that angle q." "Given a right triangle, where the length of the triangle's hypotenuse and the length of one of the triangle's other sides is known, find the measurement of the angle (q) adjacent to that other side."The function takes the form x = cos(q). Usually, q is an angle measurement and x denotes a length. The cosine function, like all trig functions, evaluates differently
depending on the units on q, such as degrees,
radians, or grads. For example, cos(90°) = 0, while cos(90)=-0.44807....
explanation |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|